1. Introduction
Modern face recognition pipelines consist of 4 common stages
- Detection
- Alignment
- Representation
- Verification
2. Detection and alignment
Detection
- OpenCV offers haar cascade and Single Shot Multibox (SSD)
- Dlib offers Histogram of Oriented Gradient(HOG) and CNN based Max-Margin Object Detection (MMOD) and Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Network (MTCNN)
Alignment
- Alignment is easy if face and eyes detected already
- But neither openCV nor dlib offer face alignment as an out-of-box function
- We have to do some trigonometry here to align faces
Retinaface is the cutting-edge face detection technology.
- It can even detect faces in the crowd and it finds facial landmarks including eye coordinates
Deepface offer both face detection and face alignment as a function. It wraps openCV’s haar cascade, SSD, dlib HoG, MTCNN and retinaface. It also does some math and trigonometry to align faces. Deepface use default configuration OpenCV’s haar cascade. `shell import numpy as np from deepface import DeepFace from deepface.commons import functions
model_name = “VGG-Face”
target_size = functions.functions(model_name = model_name)
img1 = DeepFace.extract_faces(img_path = “img1.jpg”, target_size=target_size, detector_backend =”mtcnn”) img2 = DeepFace.extract_faces(img_path = “img2.jpg”, target_size=target_size, detector_backend = “mtcnn”)
img1 = np.expand_dims(img1, axis=0) #(224, 224, 3) to (1, 224, 224, 3) img2 = np.expand_dims(img2, axis=0) #(224, 224, 3) to (1, 224, 224, 3) `
3. Normalization
Face detector detect faces in a squared area. So, detected faces come with some noise such as background color. Dlib can find 68 facial landmarks.
- We can extract face and get rid of any noise in this way.
- This optional step is called as normalization in facial recognition. MediaPipe can find 468 landmarks https://sefiks.com/2022/01/14/deep-face-detection-with-mediapipe/ https://sefiks.com/2022/01/15/virtual-background-with-mediapipe/
4. Representation
- Deep learning just appears in this representation stage.
- We will feed face images to a CNN model but the task is here is not classification.
- We will use CNN models to find embeddings similar to autoencoders.
- The most popular face recognition models are VGG-Face, Google FaceNet, OpenFace and Facebook DeepFace.
shell model_name = "VGG-Face" model = DeepFace.build_model(model_name = model_name) - These models have different input and output shapes.
- VGG-Face (224, 224, 3) -> 2622 dimensional vector
- FaceNet (160, 160, 3) -> 128 dimensional vector
- We have to pass the input shape to detectFace function in the detet and align stage.
- We must put detectFace command after input shape retrieved.

2. Why use Linux?
- - Open source
- - Linux is an open source operating system
- - Anyone, whether an individual or a corporation, can install and use Linux for free.
- - open source movement
- - Customizing
- - Linux strictly means the Linux kernel.
- - The kernel is a part of the OS that performs the core functions of the OS.
- - Only the core functions that Linux OS needs to perform are defined, and the other parts can be customized and used by the user according to his/her own use.
- - Linux strictly means the Linux kernel.
- - Stable operation
- - Since it is open source, various users can verify it in real time.

3. Linux(UNIX) Required Commands
3.1. CLI(Command Line Interface) commands
- - Made for i18n (internationalization)
- - UTF-8 is used as the default character set
- - It is recommended to use the en_US locale as it is affected by the setting of the LANG environment variable
3.1.1. File
- - Path
- - command
pwd: print working directorycd: change directory
/: root directory~: home directory-: previous directory- - Path type
- - Absolute path (abs-path): path starting from the root directory
- - Relative path: path starting from the current directory (.)
- - command
- - Check
- - command
- -
ls, file, stat, which, find
- -
- - file mode bit: 3+9 bit system representing UNIX file permissions
- - how to write
- - Symbolic mode:
- How to mark with
rwxsymbol - Consists of owner, group, and others parts, each with 3 spaces
-r: readable,-w: writable,-e: executable
- How to mark with
- - Octal mode: A method of expressing bits in octal notation
- - Symbolic mode:
- - how to write
- -
stat: outputs status of file, meta data of file- - meta data: Modifying information, not content (file name, creation time, permissions)
-
touch: update meta data of file, create an empty file if file does not exist- -
find: find directory-name filename: search for files with the same name as filename-size n: search for files of size n-mtime n: search for files with modified time n-inum n: Search for files with inode number n-max(min)depth level: Search for files with a maximum (minimum) depth of level in the subdirectory of the location to be searched- $ex1.$
find . -name '*k.data' -a -size 1M(-a: AND, -o: OR) - $ex2.$
find -name "*.tmp" -exec rm {}\;- -
*.tmpfiles are put in{} - - The meaning of
\is that the command is executed while searching one by one. - -
\+finds everything and executes the command at once
- -
- practice 1. Find general files whose contents have been changed within the last 24 hours under the current directory and save the list as mtime_b24.txt file
find ./ -mtime -1 -type f > mtime_b24.txt
- practice 2. If it goes beyond the 3rd level under the current directory, it is not searched, and all files that satisfy the condition are copied to the
~/backupdirectory.find ./ -maxdepth 3 ... -exec cp {} ~/backup \;
- - command
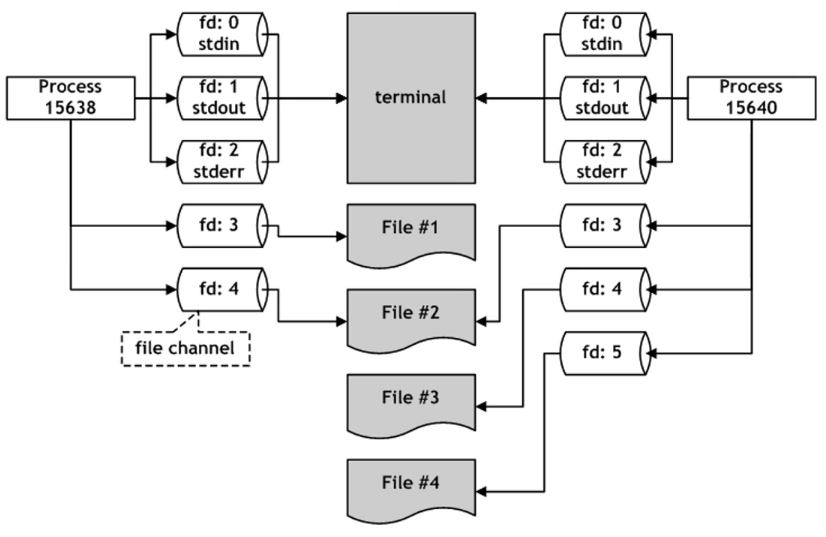
- - stdio (standard input/output)
- File channel: channel for input/output to file
- - A kind of virtualization layer that allows standardized input/output methods to be used to input/output channels to files without being directly transferred to hardware.
- - file channel: object with meta information for input/output to a file
- - Enables simplicity of I/O interface in C language
- File descriptor (often used as file descriptor, fd)
- - Unique idenfifier attached to file channels, named numerically
- - Starting from positive number 0 and increasing
- - Reserved file descriptors: 0 (stdin), 1 (stdout), 2 (stderr)
- - The fd value is given within the process. Can’t I open the same file twice?
- - Even if the same process opens the same file, a new pd value is assigned. It’s possible, but there’s a possibility of overlapping updates.
used as communication between PIPE processes
- - A type of IPC (inter-process communication)
- Anonymous pipe
- serial connection of processes
(A|B|C) - Temporarily created and destroyed pipes
- Created by using
|(vertical bar) in the shell. - $ex$.
find ~ | wc -lfind ~: find all files under the home directory|Since there is a pipe, since it is wc (word count), it is per line, so I want to know how many files are under the home directory.- The output of the find command (stdout) is concatenated with the input (stdin) of the
wccommand. - Has the same meaning as
find ~ > tmp.txt; wc -l < temp.txt; rm tmp.txt. - fd: 1 is connected to fd: 0 via a pipe
- When using the
wc -loption, the number of lines is counted.
- serial connection of processes
- Named pipes
- In Unix, the implementation of a named pipe is called a FIFO pipe.
- It is structured like a file, so there is a path+filename.
- Expresses that having a path is named.
mkfifoorPOSIX C API
- Anonymous pipe
- Redirection
- Link the direction of a channel to another place
A > B: connect (save) A’s stdout to file B- ex.
ls -a > ls.txt
- ex.
A < B: link A’s stdin to file BA >> B: direction is the same as “>”, append mode- ex.
strace ls 2> strace.txt2>means a command that connects file descriptor number 2 to a file.- Save the output of stderr, which is fd 2, to a file.
- ex.
cat: default filter to freely link stdout to files- Used to output the contents of a file to stdout
- Used to redirect input from stdin and output it to a file
- $ex$.
cat ~/.bashrc - $ex$.
cat > hello.txtThen, if you write Hello world and do^D, Hello world is entered into hello.txt and exited.
- File channel: channel for input/output to file
- - Change data
- - command
- -
cp, mv, rm, mkdir/rmdir, ln - -
mkdir: make directory - -
rmdir: remove directory (In many cases, files and directories are deleted together withrm -rfinstead ofrmdir.) - -
cp: copy - -
mv: move, rename - -
rm: remove
- -
- - command
- - Meta change
- - command
- -
chmod: change mode - -
chown, chgrp: change owner/group
- -
- - command
- - Archive
- -
tar- An archive is a grouping of multiple files.
tar -ctxv-c(create): create an archive-t(test) : test the archive-x(extract) : Extracts a file from an archive-v(verbose): output detailed information (not used in practice)f archive-file: Archive file name to input/output--exclude file: Exclude the file from the target
- $ex$.
tar c *.c > arc_c.tar == tar cf arc_c.tar *.c(just give thefoption.*.cfiles go intoarc_c.tar)
- -
- - Compress
- -
gzip, zstd- The compression rate is
xz > bzip2 > zstd > gzip > lz4 - xz: Compression rate is good, but slow.
- zstd: used a lot these days $ex$. The classic way to use tar and gzip together
- compression:
tar c /etc/*.conf | gzip -c > etc.tar.gz - release:
gzip -cd etc.tar.gz | tar x
- The compression rate is
- -
3.1.2. Text
- - Editor
- -
vim(vi)
- -
- - Filter
- -
cat(tac), head, tail, less/more, sort
- -
- - Regex
- -
grep, sed, awk
- -
3.1.3. Job control
- -
jobs, fg, bg
3.1.4. Process control
- -
kill, pkill, pgrep, strace(tracing)
3.1.5. Networking
- -
nc (net cat), curl, wget
3.1.6. Disk
- -
df
3.1.7. System
- -
free, top, ps, pidstat, lshw
3.2. Admin commands
3.2.1. Package
- - Redhat:
rpm, yum - - Debian:
dpkg, apt
3.2.2. Network
- - status:
ss,netstat(old fashion) - - config:
nmcli,ip - -
ssh - - packet:
tcpdump, wireshark, tshark
3.2.3. Files and kernel
- -
lsof - -
sysctl
3.2.4. Disks
- -
fdisk, parted, mkfs, mount, lsblk, blkid, grubby, udisksctl
3.2.5. User
- -
useradd, groupadd, usermod - -
passwd, chpasswd






![[Paper review] Self-correcting LLM-controlled Diffusion Models](/assets/images/blog/post-5.jpg)